一、Redis3.0与3.2文件对比
1. clone redis
|
|
2. checkout分支
|
|
3. 比较
(1) 比较3.0和3.2文件变化数
|
|
(2) 比较3.0和3.2文件变化统计
二、Redis3.0与3.2默认配置文件变化
1.配置变化
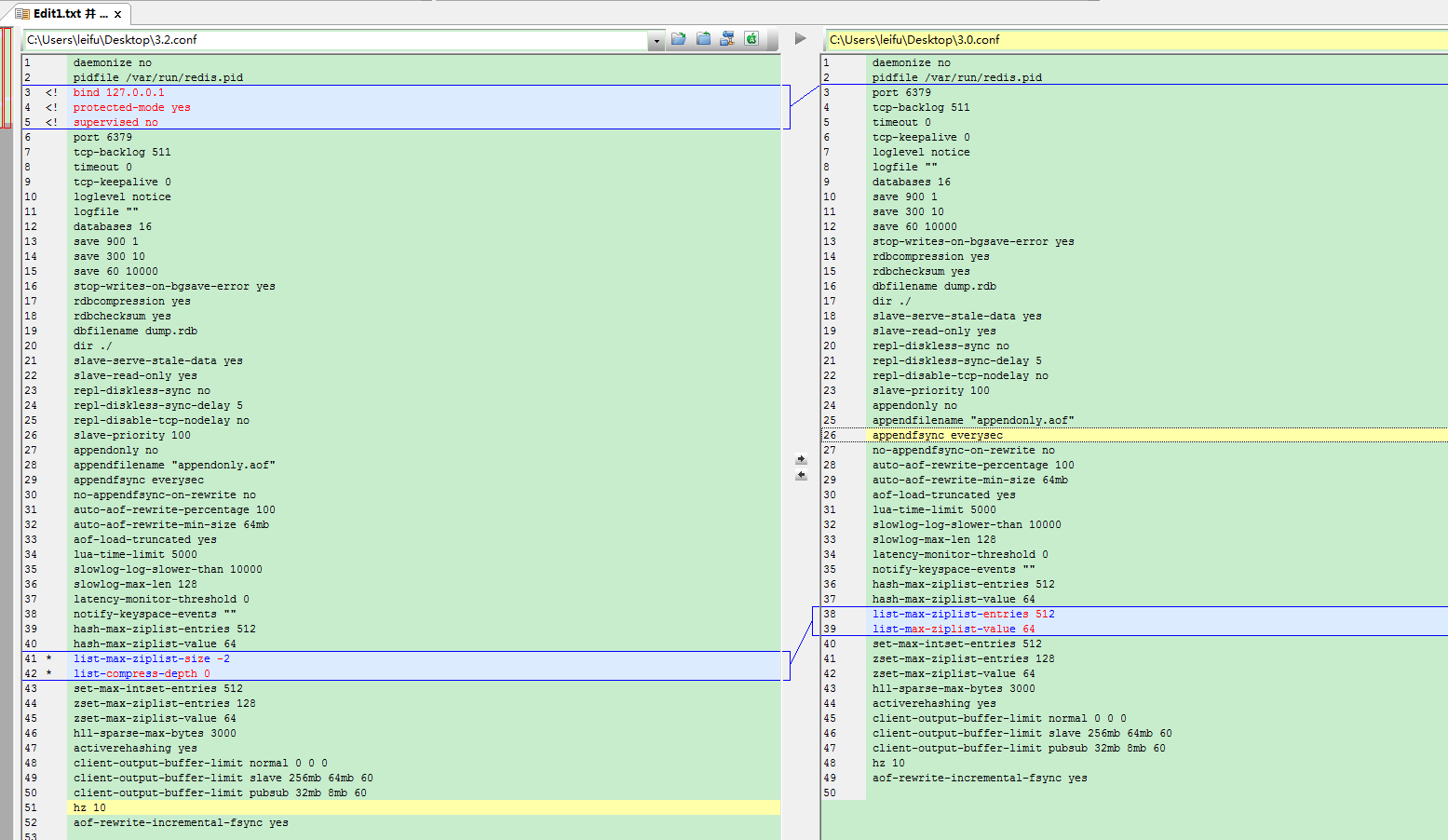
Redis3.2添加了两个配置:
- protected-mode yes
- supervised no
Redis3.2修改了两个配置:
有关list的优化,由(1)改为(2),虽然还没详细了解,应该是list的底层数据结构做了一些新的变化或者优化。
配置一:
配置二:
配置三:
bind在Redis3.2.0中默认改为127.0.0.1
2.新配置说明
- (1).protected-mode(默认是yes)1234567891011121314151617# Protected mode is a layer of security protection, in order to avoid that# Redis instances left open on the internet are accessed and exploited.## When protected mode is on and if:## 1) The server is not binding explicitly to a set of addresses using the# "bind" directive.# 2) No password is configured.## The server only accepts connections from clients connecting from the# IPv4 and IPv6 loopback addresses 127.0.0.1 and ::1, and from Unix domain# sockets.## By default protected mode is enabled. You should disable it only if# you are sure you want clients from other hosts to connect to Redis# even if no authentication is configured, nor a specific set of interfaces# are explicitly listed using the "bind" directive.
说明
用一段代码就可以说明什么是protected-mode
1234if (protected-mode && !requirepass && !bind) {Allow only 127.0.0.1,::1 or socket connectionsDeny (with the long message ever!) others}其实设置成默认是为了保护对redis不了解的人,提供安全性,但是对于对于不需要bind和requirepass的使用者(例如内网),需要将protected-mode设置为no
- (2).supervised(默认是no)123456789# If you run Redis from upstart or systemd, Redis can interact with your# supervision tree. Options:# supervised no - no supervision interaction# supervised upstart - signal upstart by putting Redis into SIGSTOP mode# supervised systemd - signal systemd by writing READY=1 to $NOTIFY_SOCKET# supervised auto - detect upstart or systemd method based on# UPSTART_JOB or NOTIFY_SOCKET environment variables# Note: these supervision methods only signal "process is ready."# They do not enable continuous liveness pings back to your supervisor.
说明
可以通过upstart和systemd管理Redis守护进程,这个参数是和具体的操作系统相关的。
- (3).bind (Redis3.2.0中bind默认是127.0.0.1)12345678910111213141516171819202122# By default, if no "bind" configuration directive is specified, Redis listens# for connections from all the network interfaces available on the server.# It is possible to listen to just one or multiple selected interfaces using# the "bind" configuration directive, followed by one or more IP addresses.## Examples:## bind 192.168.1.100 10.0.0.1# bind 127.0.0.1 ::1## ~~~ WARNING ~~~ If the computer running Redis is directly exposed to the# internet, binding to all the interfaces is dangerous and will expose the# instance to everybody on the internet. So by default we uncomment the# following bind directive, that will force Redis to listen only into# the IPv4 lookback interface address (this means Redis will be able to# accept connections only from clients running into the same computer it# is running).## IF YOU ARE SURE YOU WANT YOUR INSTANCE TO LISTEN TO ALL THE INTERFACES# JUST COMMENT THE FOLLOWING LINE.# ~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~bind 127.0.0.1
说明
bind在Redis3.2.0之前默认是0.0.0.0或者说””,为了保证不太了解Redis安全性的人,在Redis3.2.0中bind默认是127.0.0.1,也就是只有本机回环地址可以访问。如果需要配置sentinel、cluster或者需要机器机器可以访问该Redis实例请修改为0.0.0.0或者指定的内网IP.
(4).list-max-ziplist-size(默认-2)
12345678910111213# Lists are also encoded in a special way to save a lot of space.# The number of entries allowed per internal list node can be specified# as a fixed maximum size or a maximum number of elements.# For a fixed maximum size, use -5 through -1, meaning:# -5: max size: 64 Kb <-- not recommended for normal workloads# -4: max size: 32 Kb <-- not recommended# -3: max size: 16 Kb <-- probably not recommended# -2: max size: 8 Kb <-- good# -1: max size: 4 Kb <-- good# Positive numbers mean store up to _exactly_ that number of elements# per list node.# The highest performing option is usually -2 (8 Kb size) or -1 (4 Kb size),# but if your use case is unique, adjust the settings as necessary.(5).list-compress-depth(默认是0)
1234567891011121314# Lists may also be compressed.# Compress depth is the number of quicklist ziplist nodes from *each* side of# the list to *exclude* from compression. The head and tail of the list# are always uncompressed for fast push/pop operations. Settings are:# 0: disable all list compression# 1: depth 1 means "don't start compressing until after 1 node into the list,# going from either the head or tail"# So: [head]->node->node->...->node->[tail]# [head], [tail] will always be uncompressed; inner nodes will compress.# 2: [head]->[next]->node->node->...->node->[prev]->[tail]# 2 here means: don't compress head or head->next or tail->prev or tail,# but compress all nodes between them.# 3: [head]->[next]->[next]->node->node->...->node->[prev]->[prev]->[tail]# etc.
说明
Redis3.2.0引入了新的quicklist的数据结构做了list的底层存储方案。废弃了原来的两个配置参数,list-max-ziplist-entries和list-max-ziplist-value
|
|
在Redis3.2.0中设置原来的参数已经不生效了,应该是无法使用了。
有关quicklist的详细使用还需要查询文档和源码来研究
三、 Redis3.0与3.2关于Cluster的一些变化(来自3.2-release-notes)
原文:
Redis3.2.0的cluster完全兼容Redis3.0,也就是说可以混合部署组成集群,在Redis Cluster上Redis3.2.0没有做什么新的技术,但是也有一些比较重要的事情:
- Redis Cluster均衡(应该是指redis-trib.rb中实现类将slot进行负载均衡的功能)
- 提供了一个基于流水线的migrate命令,用于水平迁移数据,速度是原来的10倍多。
- 提升了从几点迁移的功能。
- 在quicklist这种新的数据结构的帮助下,在节点之间迁移大的big list快了很多.
注意:上述特性均在Redis3.0.7有体现,如果对于Redis3.2.0不太放心的话,可以使用Redis3.0.7。
四、 Redis3.0与3.2关于Sentinel的一些变化(来自3.2-release-notes)
原文:
Sentinel connection sharing不太了解,看着像是添加新的sentinel节点后,可以共享其他sentinel节点的master,对于sentinel监控多个master比较有用,这样扩展sentinel节点时候比较方便配置,有关这个后面会继续试验。- 提供info-cache命令
有关Sentinel,3.2.0完全向后兼容3.0
####